Everything You Should Know About Augmented Reality
IT magazines have several terms about futuristic technologies that make a layperson wonder. Flipping through the pages of such magazines, you might also have come across a few of those jargon. Do you also wonder about their functionalities? Then this blog is for you!
Some of those terms include:
- Superimposition
- Haptic communication
- Augmented Reality
- Head-mounted gears and displays
- Smart glasses
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- Mobile computing
- and more. As the list of digital trends keeps increasing, you feel worried about how to catch up with them all.
For many, AR or VR are abstract or outlandish technologies we are still unfamiliar with. We have only seen them in big-budget Hollywood sci-fi movies and are yet to experience them in real life. But, the fact is:
- Virtual 3D models
- Immersive displays with interactivity features
- Animated holograms etc.,
- are no longer futuristic. Modern-age Industry 4.0 has already started leveraging these technologies to enhance UX. This article will talk about the features of AR that will give an in-depth insight into the subject.

Augmented Reality (AR): The Concept and Its Working
AR is a technological breakthrough facilitating the expansion of the physical world with digital information layers over it. It is semi-immersive and is different from VR. VR or Virtual Reality creates a complete artificial ambiance replacing the real world with a virtual replica.
AR enhances user experience with video, sound, multimedia elements, graphics, etc., in the existing environment. The superimposition of CGI (Computer-generated imagery) over the physical environment, thus modifying and enhancing the reality perception, is called AR.
The term was phrased in 1990 and was first used commercially for military and television shows. As smartphones and the Internet became more accessible, consumers expected greater interactivity. AR served this purpose of heightened user experience. We now have multiple AR apps that impact our lifestyle, shopping experience, entertainment, and more. Customer behavior and usage patterns are also impacted by augmented reality technology. Direct projection of 3D models on physical objects makes this happen, changing our perceptions. The models are projected or "digitally overlayed" over the real environment, thus "augmenting" the user's view.
Digital animation is particularly connected by AR apps to a specialized ‘marker’. The GPS embedded in smartphones is also used for pinpointing specific locations. Augmentation takes place in real-time in the context of the particular event being focused upon. While watching a live cricket match, you must have seen scores or stats overlaid on the ground. This is a typical example of AR.
Working of the Augmented Reality Technology
We are often interested in understanding the technical aspect of the functioning of Augmented Reality. To enable AR features, data from pictures, videos, animations, and 3D models are used. The results can be displayed in natural as well artificial perspectives. While viewing AR results, you would stay aware of the real-world features made possible by computer vision. This feature is missing in VR.
For displaying AR results, you can use glasses, handheld systems, smartphones, screens, head-gears, or other suitable devices. Advanced technologies such as ‘simultaneous localization and mapping (S.L.A.M.)’ and depth tracking are used. For tracking depth, data from the sensor is used to calculate the distance to the targets.
Other components are also used in AR. They include:
- Cameras & sensors
These are used to gather information about user interactions to process the same. The surroundings are scanned by cameras mounted on devices. The AR devices use the information to locate physical objects and generate 3D models. Images/videos can be captured using smartphone cameras or special cameras, such as Microsoft Hololens.
- Processors
Augmented reality devices essentially function as small computers, like contemporary smartphones. Processors in them measure speed, orientation in particular direction, angle, and other parameters. Processing uses CPU, GPU, RAM, flash memory, GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other elements.
- Reflectors
To facilitate the proper viewing of virtual images by human eyes, AR devices come installed with mirrors. Some have several miniature curved mirrors installed in them. While others have double-sided mirrors to reflect light to the cameras and human eyes. The reflection paths are built to align the created images properly.
Different Augmented Reality Types
- Marker-Based
This is also known as image recognition-based AR. A specialized visual object is needed, which would be scanned by a camera. The marker can be printed QR code, a particular sign, or anything. The AR device also calculates the marker’s location and orientation for positioning the content. Digital animations are initiated by the marker for viewing by users. As such, magazine images may suddenly transform into 3D models when markers are triggered.
- Markerless
This AR type is also called position-based or location-based AR. The user's location data is provided by a compass, accelerometer, GPS, and gyroscope. The data is used for assessing the type of AR content available in a particular area. When viewed over the smartphone, this AR type usually generates maps, directions, and info about businesses in the locality. Different applications consist of pop-ups about business ads, support for navigation, information about events, etc.
- Projection Based
In this AR type, synthetic light is projected onto the physical surfaces. In certain cases, the light is allowed to interact with the surface. The AR effect is in the form of holograms which we have come across in Star Wars and other science fiction films. User interaction with the projection is detected by modifications in positions.
- Superimposition Based
Here, the original view is replaced with complete or partial AR. The concept revolves wholly around object recognition. Like in the IKEA catalog app, the model of superimposed AR is visible. Users can position virtual furniture substitutes in the room within the catalog.
Devices for Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is getting further evolved and is supported by different contemporary devices. Some are handheld devices, smartphones, tablets, Google Glass, and similar gadgets.
AR hardware or devices process and project images with:
- Cameras
- GPU
- CPU
- Sensors
- Accelerometer
- Digital compass
- Gyroscope etc.
AR can be experienced using different devices, as discussed below.
- Mobile Devices

These include tablets and smartphones on which AR-related mobile apps can be run seamlessly. Different AR functionalities exist for games, entertainment purposes, sports, social networks, business analytics etc.
- Specialized AR Devices
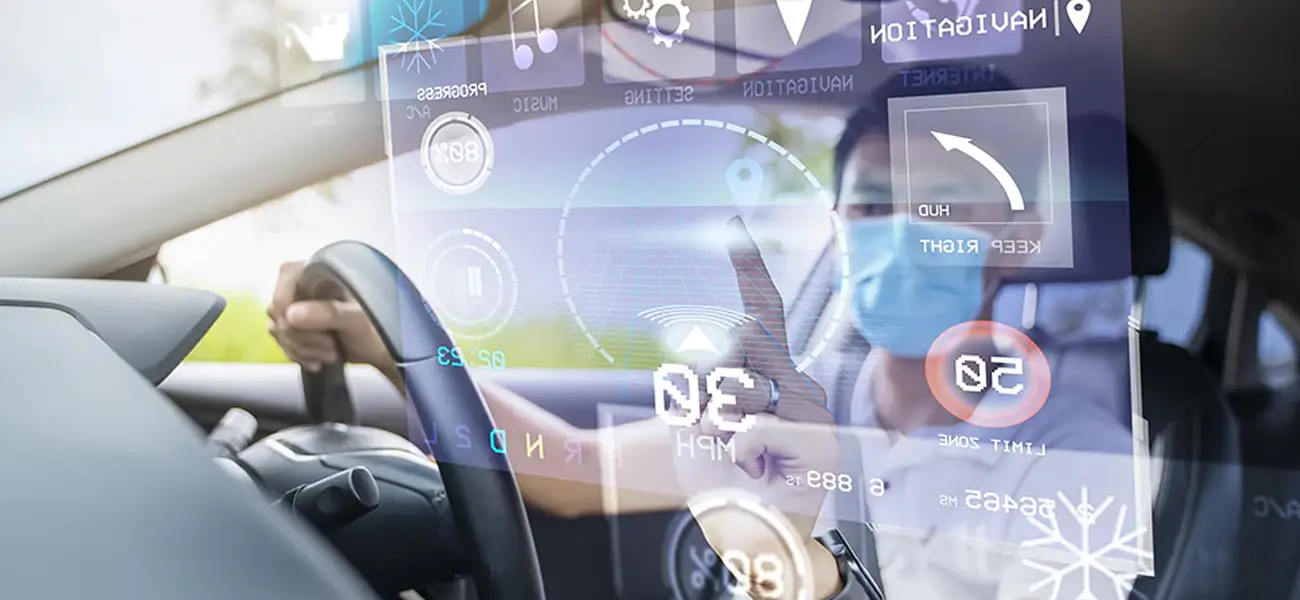

These devices are manufactured mainly for experiencing augmented reality. The HUD (Head-Up Displays) is a typical example of this. Data is sent directly to a transparent display for viewing by the user. The devices were initially used for training military pilots of fighter planes. These devices are now used in automotive, aviation, production, sports, and other industries.
- Smart AR Glasses

Such glasses include Meta 2 Glasses, Google Glass, See-Thru from Laster, AR eyewear from Laforge, and others. Notifications can be displayed by the glasses directly from the user’s phone. They can assist workers on assembly lines by showing content in hands-free mode.
- Smart Lenses
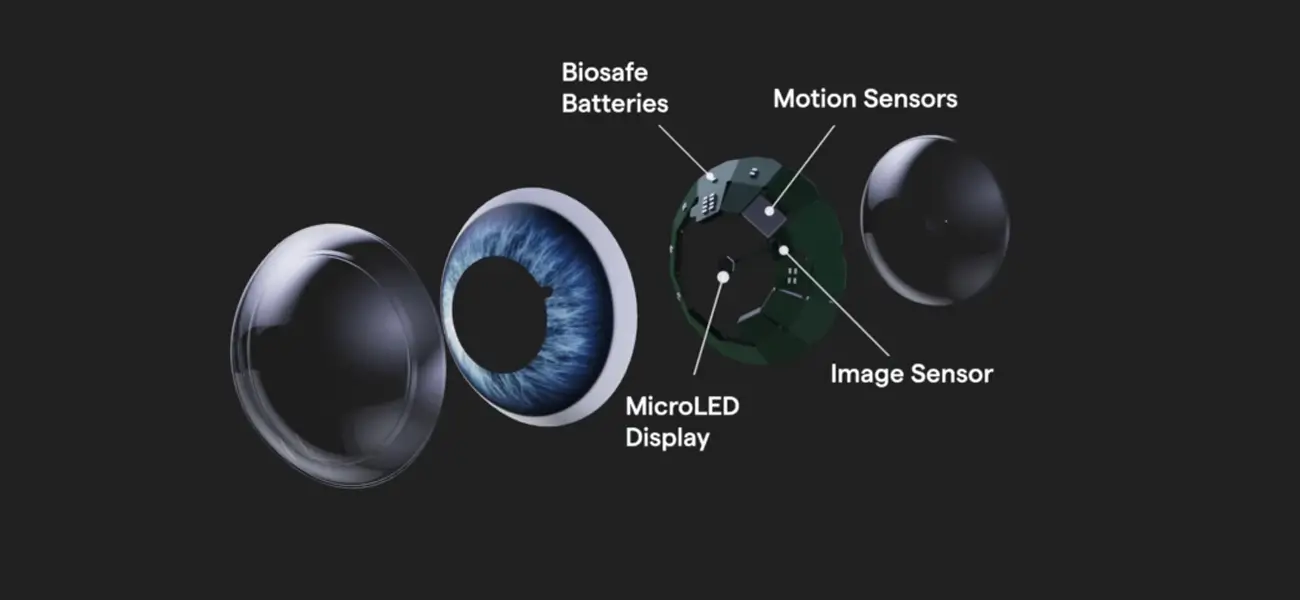
The AR contact lenses take the AR experience to the next level. AR lenses are being developed by Samsung, Sony, and other manufacturers. In the case of Samsung, these lenses are being developed for accessorizing their smartphones. Sony, in contrast, is developing the lenses as a standalone AR device. This would facilitate capturing images and data storage.
- VRD or Virtual Retinal Displays
Images are created by these displays through the projection of laser light directly to human eyes. The images are high resolution, bright, and in high contrast. The displays are still to be manufactured for practical purposes.
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality finds practical applications in different segments like:
- Education
- Furniture Retailing
- Tourism
- Retail Business
- eCommerce
- Healthcare and medicinal segments
- Jewelry manufacturing
- Manufacturing
- Sports
Augmented Reality related software programs have been designed enthusiastically in recent years. After the release of products such as Google Glass, the attention on AR devices has been renewed.
In real-world contexts, AR’s usage has many examples. The education domain can get a facelift with AR applications. Augmented reality technology apps are being designed for:
- Embedding pictures and
- Textual content and videos on syllabus curriculums
In the advertisement and printing sectors, certain apps are being developed. These can display digital content atop topics in real-world magazines.
AR would empower tourists to secure information about historical places in real-time. This happens only by directing the viewfinder of cameras to the monuments.
Translation apps can be developed using AR. These apps can interpret and translate texts in different languages to your native dialect.
AR apps are also deployed for offering location-based services. For their current locations, users can secure relevant info about nearby places. Information about places can be obtained, and users can read the reviews posted by others.
Unity 3D Engine is being programmed for developing AR-underpinned 3D games playable in real-time.
How would AR Shape the Future?
Advanced technologies and digital trends are surfacing almost every day. Recently, Virtual reality has made steady inroads in different sectors. Out of all the modern advancements, AR is one technology that will continue to stay and will be integral to our daily lives. The existing ambiance is used by AR for overlaying extra info atop that.
You can think about Pokemon Go, which caused ripples online after its release. It is an example of an AR experience. In the game, players are entrusted with fighting digital monsters. In social media apps like Facebook, Snapchat, or Instagram, AR-based filters are offered for overlaying animated pictures on the user's face.
You might be wondering about the future of AR and how it will be reshaping and transforming different industries. Industries stand to benefit a lot by availing of the developments in AR.
Uses of augmented reality technology in various industries
Working of AR Technology
- Real Estate Domain
We all aspire to live in beautifully designed homes that complement our lifestyle and preference. Augmented reality has the potential to make this ambition come true. The AR technology interactively uses CGI during the planning stage. This allows buyers to visualize how the finished apartments will finally look like. From the real estate industry's perspective, the technology converts 2D models into 3D models. Assets such as property images and blueprints are converted into 3D renders. This facilitates ease of interaction by buyers. Realtors can display properties conveniently by offering a semi-immersive experience to the buyers.
- Online Shopping
Conventional shopping is gradually being replaced by online shopping. The uncertainty factor still prevents most customers from trusting products online. With AR, the shopping industry can be given a facelift to motivate prospective buyers to engage in online shopping. AR allows consumers to view the products realistically in the chosen environmental setting. Also, AR glasses can be provided at each retail shop or supermarket to enhance the shopping experience. The glasses can be used for displaying info related to prices, designs, product specifications, and the like.
- Travelling Industry
The uses of AR can be seen in the travel industry also. It complements virtual reality in a way that is already being used in the travel domain. Smartphone-driven AR apps can be deployed to help out tourists in many ways.
- Checking and finding local attractions
- Figuring out the best travel routes
- Translating signboards and signages in a foreign language to the tourist's native language.
The traveling experience can also be enhanced with AR implementation. AR can make exploring local attractions, zoos, or other places more exciting. The 3D models of the attractions and landmarks can be displayed to showcase the history of the place and its evolution. AR can also be used to better educate the travelers about the details of the place.
- Healthcare Industry
AR can also be used in the healthcare industry and pharma to save lives. Already, VR headsets are used to transport patients to a 3D non-existent world for relieving pain. AR can also be leveraged to make the existing processes more failsafe. Surgeons can use AR to gain insights into the risks inherent in invasive surgeries. Further, they can utilize the insights in actual surgeries, making them full-proof. Earlier, several monitoring devices were required to display patients' vital statistics. One of them is an endoscopic camera. It is quite a painful process for the patient during the endoscopy. However, with AR-driven smartglasses, surgeons can easily get the statistics and readings. This prevents the patient from suffering unnecessarily.
- Educational Domain
The way students learn can be transformed using AR. Immersive content can help students understand the concepts better. 3D models can be created to help students easily comprehend complex information. This way, they can gain insights into topics from a broad perspective. Museums, art galleries, and historical places also incorporate AR technology. It helps to exhibit the collections dynamically to visitors and educate them. This increases the excitement factor among the audience because they can see the history. Since AR focuses on exploration, students become more interested in the learning experience. Thus, the educational industry can benefit from AR technology significantly.
Conclusion
Augmented reality has immense potential for reshaping various industries offering better user experience. It is growing exponentially as more and more devices adapt. The technology can develop in a standalone manner or collaboration with AI. As technology advances, the efficiency and quality of AR technology is also bound to grow.
Many big brands utilize AR-compatible 3D models to give their audiences a better shopping experience. These digital models are compatible with web-based AR and overlayed in real-life environments. The best part is no separate gadget is required to view the models. Professional 3D modeling companies can develop such AR-compatible models with the utmost quality.
- Real Estate Domain