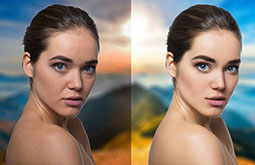What is prepress? Everything You Need to Know
Whether it is for traditional prints like magazines, novels, newspapers, and the like or graphic designs such as brochures, billboards, or banners, the prepress process is paramount. Although the print era demands certain technical alterations to the traditional prepress process for offset printing, the ultimate idea remains the same. To make the final outcome print-ready and ideal for publishing.
If you are a beginner to the concept and want to learn more about the digital prepress process, its importance, and how it is done, stay with us until the end. This article presents a step-by-step guide about the formatting process prior to publishing and how the raw manuscripts are transformed into international bestsellers. Let’s take a ride into the world of print media and printing preparation.

What is prepress?
Prepress is a very crucial stage when a raw file is prepared, formatted, and checked with accuracy for any typos, alignment issues, or any other technical errors. This is one of the most essential stages in the publication operation and must be done with great accuracy and precision. These technical steps of preparing the artwork lead to the final printing; in short, it is sort of a preparation before a big event.
Just after the client shares the requirements and the art files for production, the prepress formatting stage begins. There are several advanced software required for this; most professional companies that offer high-end prepress services leverage these software programs. So, it is always better to work with a professional team to get a flawless prepress conversion outcome.
Different prepress techniques are utilized before a document is published, and the outputs are usually in PDF formats or other suitable file types with different file sizes. The most common techniques are pre-flighting, digital content structuring, creating high-quality image files, and so on.
What is prepress in graphic design?
The availability of digital graphics has made publications more exciting and visually appealing. To ensure graphics and illustrations in e-magazines, eBooks, brochures, flyers, and other digital texts are accurate, prepress plays a vital role. If the graphics are below par, the quality of the publication degrades.
Without dedicated prepress preparation, the graphics will be of low resolution. There can be major color mismatches, margins, bleed areas, typography that may not meet the expected specifications, and so on. Therefore, the prepress process for graphics has to be accurate to look professional.
The process is also called pre-media. It mainly involves preparing digital files to turn them into top-notch-quality prints that meet the desired specifications. A substantial creative and technical sense is required for the job. Leading graphic design tools like Adobe InDesign, QuarkXPress, Microsoft Publisher, etc. are used to create the basic layout for such DTP work.
Photoshop is an amazingly powerful software and its is built with lots of useful tools that can be utilized to adjust image resolution, making it ideal for high-end printing. This is extremely helpful while making last-minute changes to the photo just before the final printing and enhancing the image resolution. Check out the simple and insightful guide below and get started.
What is prepress in printing?
The prepress, or pre-media, process in DTP printing is similar to the process involved in graphic design. It refers to the precise preparations and procedures made for a digital text file before it is passed on to the final printing system. The print can be used for different digital purposes. Therefore, it should be accurate and easy on the readers’ eyes. The flow must be linear, and no typography or text errors should be in the body copy.
An expert in DTP publishing typically completes the process using cutting-edge tools to guarantee that the artwork is ideal for the printer's technical requirements.
The entire process includes formatting and creating vector artwork that is aligned with the customer’s objectives. The graphic artworks must be responsive, meaning they must be adaptable to any device they are viewed on while retaining the image quality. The process also involved adjusting color schemes, given the difference between offset print and DTP publications. In print materials, color profiles are usually CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black). Whereas, digital files use the RGB (Red, Green, and Blue) color profile.
Therefore, robust color management is done during this process to guarantee perfection and consistency in the hues and shades. Also, file preparation is another crucial step in digital print production. It ensures file formats meet the printing requirements; the graphics do not appear in low quality, and so on.
The importance of the prepress process
Anyone in the printing industry or publication services knows how significant the prepress phase is for publishing. Simply put, it can make or break the outcome of a digital text. Millions of authors, novelists, comic book creators, publishers, journalists, academics, research scholars, entertainment media houses, PR agencies, and other literary personnel, as well as corporates, require billions of publications each month, sometimes even each week. Every one of them has varied objectives and specific instructions for their publications.
Only a flawless prepress process can cater to all the different demands and make the journey from raw manuscripts to engaging prints seamless.
These days, there has been a rise in self-publishing, which makes prepress all the more vital to ensuring the final printed material replicates the original version. For this, the guidance of professional service providers for the process of prepress is mandatory.
What are the key stages in prepress?
As mentioned earlier, quite a few technical steps are being undertaken to make a file print-ready for publishing. In this section, let’s take a broader look at the technical stages of prepress and discuss them in further detail.
Proofreading
Proofreading, or checking for grammatical errors and typos, is the first step in preparing files for printing. No author, publisher, or digital marketer wants their publications to be full of errors. However, almost more than 3% of these errors are detected at this stage. Then, skilled proofreaders carry out a careful round of review to correct these flaws.
Copyediting
Often, text manuscripts have specific errors that the original author overlooks. Be it a novel, a fiction, a magazine copy, or a corporate write-up, a lack of proper flow, incorrect word choice, or incorrect sentence formation renders the publication of low quality. Any of the mentioned discrepancies found in a publication degrades the reputation of the author as well as the publishing house.
Hence, copyediting is a vital step. An experienced copyeditor not only improves these aspects but also elevates the quality of the manuscript, reduces ambiguity, creates a natural flow, and more. Sometimes, it even requires rewriting certain portions of the text with the consent of the original contributor.
Adjusting alignment and font spacing
This is another pivotal aspect of a foolproof prepress typesetting and formatting procedure. The spacing between the fonts, as well as the letters that are called “kerning”, must be accurate. It must also be consistent throughout the body text.
Kerning determines the optimal space and balance between individual characters. It also plays a significant role in the overall readability and appearance of any text, be it a novel, a journalist’s material, or a corporate write-up. Advanced software and tools are required to adjust these automatically, which gives a professional look to the final draft.
Adjusting image resolution and size
Avoiding any pixelation issues is the most critical thing all prepress formatting technicians must take care of. With meticulous image resolution adjustments from low to high, the final drafts are created before the files are passed on for DTP production. Images must be made ideal for web viewing with an optimized file size for fast loading.
They must also be responsive to adapt to the varied devices the texts will be read on. Flawed image size and resolution imply unnecessary extra reprints, which means massive additional production costs. Therefore, this process holds great significance for the overall success of a book for the author as well as the publishing house.
The ultimate prepress checklist to bookmark
Our final segment presents a flawless prepress and pre-media production checklist. In order to avoid costly mistakes, prepress technicians must be thorough with the prepress tips and tricks required. Keep this checklist bookmarked for your ready reference, and impress your clients with an optimized workflow.
Conclusion
Traditional printing requires a combination of creativity and technical expertise. When the correct balance is struck between the two, one can rest assured that their production will stand out in the crowd. As this insightful article detailed everything, quite a lot of technical stages are involved in the process to ensure the final prints are of high quality and become a best-seller, crossing boundaries.
So, get yourself an experienced and expert provider offering high-end prepress services. These external agencies are accomplished in their domains and offer the best competitive price. Their turnaround time is also the shortest. Consult a prepress conversion expert today. Good luck!