3D modeling has become one of the most discussed and applied technologies in recent years. Given its multiple benefits, applications across many sectors, and visual accuracy, more aspiring professionals are keen on learning this fantastic technology. If you are also one of those 3D enthusiasts and want to learn more about it, you are just in the right place. This article will act as a guide and answer the following:
- What is 3D modeling?
- The various types of 3D modeling and how they differ from each other
- What are the multiple applications of 3D technology?
- Some of the most common 3D file formats

So, be ready to explore the world of 3D modeling and learn all the nitty-gritty of it. Let’s begin!
What is 3D modeling?
3D modeling is the computerized process of developing three-dimensional mathematical representations of an organic or inorganic object. This complex technical process is done through specialized computer programs and software applications. The modeling process involves the manipulation of the vertices, edges, and polygon structures within a 3D simulated space or environment.
In a nutshell, creating 3D models through advanced software is deemed as 3D modeling.
3D models are vertices that bind together and form a mesh. Vertices are points in a 3D space that define the shape of a 3D model. The mesh is the core, or the very foundation, of any 3D model. The shape of each vertex or point can be altered to develop a 3D digital model. The 3D software program uses coordinates to identify the location of each horizontal and vertical point that is relative to a specific reference point in the 3D space.
The different types of 3D modeling techniques
Before moving on to the uses and applications of this marvelous technology, let us first understand the different techniques involved in the 3D model creation process. In this article, we have compiled a list of 10 such techniques that will guide any aspiring 3D professional.
Some of these are considered the most commonly used techniques, involving less complexity and effort. And some fall under the more complex ones. We shall discuss all these while maintaining an unbiased approach. Let’s start!
-
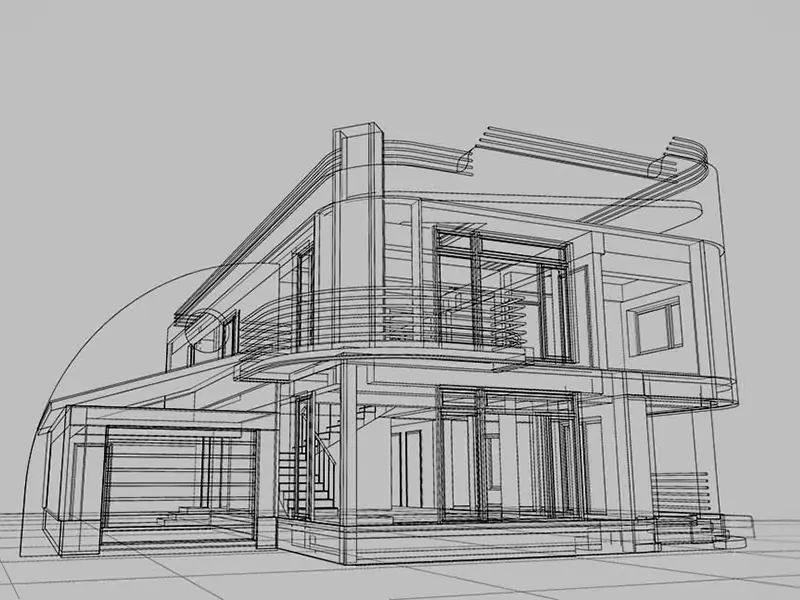
Wireframe Modeling

Wireframe 3D modeling is a common technique leveraged by most 3D modelers that demonstrates a basic structure of the modeled subject. In this method, the representation is mainly done through lines, curves, and edges without focusing much on the details. This technique is best for creating 3D prototypes and testing concepts that demand superfast turnaround and design iterations.
-
Surface Modeling

Another simple yet highly effective technique, surface modeling, showcases the outward view of the model. The models created via this technique are usually more detailed than wireframes and depict some basic details. Such as the organic shapes and features that are impossible to view in a skeletal (wireframe) model. Unlike the first technique listed above, surface modeling uses mathematical equations to create the design and texture of the physical models. The physical models can have any kind of surface ranging from opaque, semi-opaque, hollow, solid, deformable, soft, plastic, etc.
-
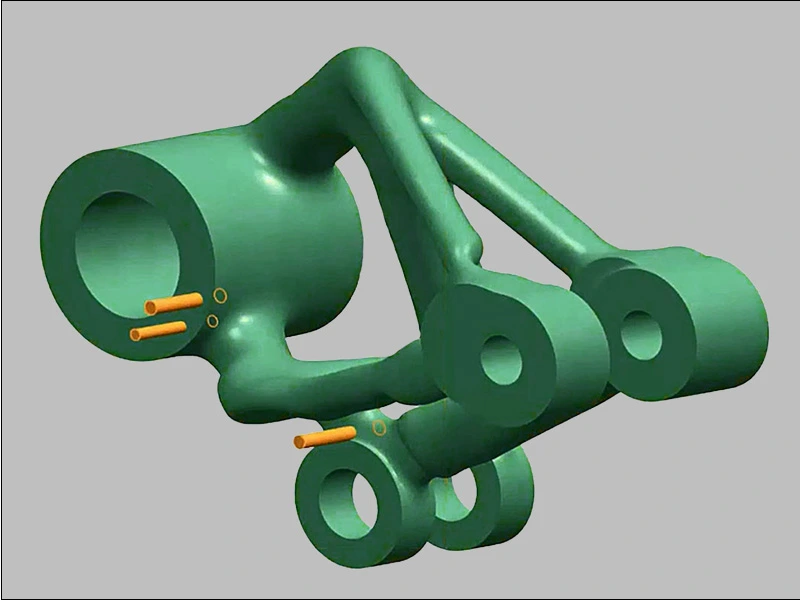
Solid Modeling

By popular opinion, the solid modeling technique is one of the most popular and commonly utilized by 3D specialists. Professional 3D modelers use this to create a true volume in the digital model, using lines, points, surfaces, and curves. The models generated by this technique can be modified, rotated, digitally manipulated, or clumped. Though the angles remain solid and don’t get affected by any deformation. Basic geometric shapes like cylinders, pyramids, spheres, cubes, and cuboids are used for this technique, along with their mathematical equations, to create a high level of accuracy.
-
Primitive Modeling

This technique bears a striking similarity with solid modeling (discussed above), as it involves substantial usage of 3D primitives. 3D primitives are nothing but simple geometric shapes in the world of 3D design. Shapes like circles, spheres, cones, cubes, cuboids, cylinders, and tubes - are the common types of 3D primitives used in this particular 3D model design process. 3D designers combine these shapes or subtract one from the other to create a completely different, new shape.
-
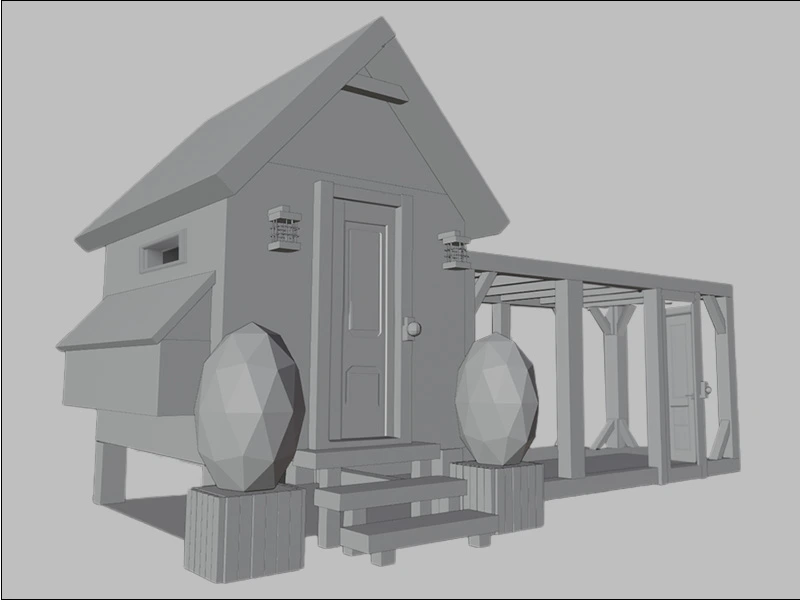
Box Modeling

Another considerably simple technique, box 3D modeling, uses 3D primitives like boxes and spheres to generate the final model. Modeling experts use these simple shapes as the foundation for the basic shape. They eventually add further details to give the actual shape. A simple box or cube primitive can be pulled, manipulated, scaled, or stretched to create the basic shape of the model by adding other boxes. This basic shape can finally be sculpted into an interesting shape.
Some of the advanced modeling techniques
As mentioned earlier, we will also discuss a few relatively advanced 3D modeling techniques in this list. These techniques have quite complex workflows and are to be done only by professional 3D modeling agencies with experts. They offer high-end 3D design services using cutting-edge technologies. Hence, it is easier for them to execute these advanced techniques with technical prowess.
Check out the following:
-
Polygonal Modeling
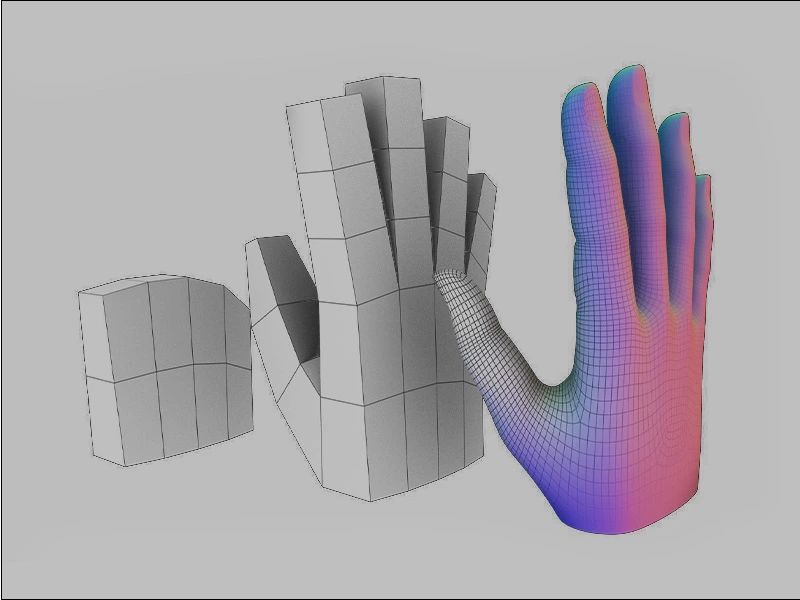
The polygonal 3D modeling process is one of the most sought-after processes among 3D artists. Partly because this technique allows the creation of accurate, organic, and unique designs. These correctly resemble humans, animals, and other organic living beings. Due to this, the polygonal technique is mainly used to create 3D assets for video games. In this technique, a polygonal mesh or patchwork made of geometric figures is made and then gradually given the shape and details of the physical model. These details are added mostly by splitting the geometric shapes at accurate angles and perspectives.
The number of polygons added to the mesh determines the resolution of the final model. If the polygons are larger, it is high-poly. If it is fewer, then it is called low poly.
-
Rational B-Spline (Basis Spline) Modeling
The rational B-spline 3D modeling technique involves mathematical equations representing analytical shapes, like conic curves, circles, free-form curves, etc. The “B” stands for basis,” per the numerical analysis. The rational b-spline technique generates accurate shapes under projective transformations. The initial basic shapes created in the method can be further generalized to patches that can represent shapes like quadrics, tori, and planes.
-
Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline/Basis Spline (NURBS)
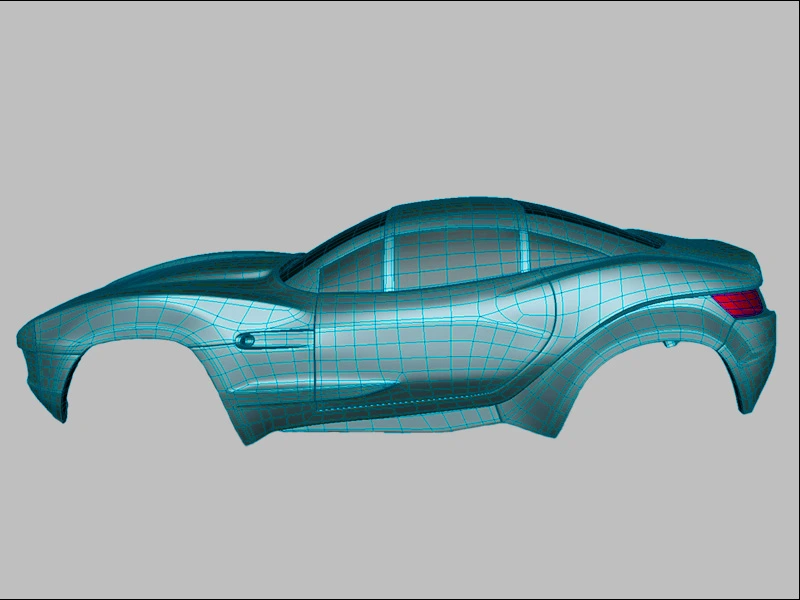
A counterpart of the RBS (rational B-spline modeling, discussed above), the non-uniform rational B-spline or NURBS, is another intricate mathematical model. The NURBS modeling technique is crucial for CAD software as it allows 3D modelers to create ultra-realistic 3D rendered models of rounded objects. It has been subsequently adapted by the automobile and aeronautics industries.
Complex automobile shapes and aircraft designs can be created and given their final shape with this technique. NURBS modeling is mainly popular because it creates perfect curves out of free-form, rounded shapes with organic slopes and forms. Moreover, the NURBS geometry is fairly easy to manipulate to any precise form or shape the user wants instead of relying on pre-defined parametric shapes.
-
Digital Sculpting
Another complex multi-layer 3D modeling method, digital sculpting, is usually utilized to create highly organic 3D models. 3D modelers pinch, pull, stretch, smooth, and grab the digital object like a real-world sculptor working on real clay. Advanced software applications are required for the 3D sculpting process, which simulates digital clay and enables carving. It is a time-consuming and laborious process that only highly experienced 3D experts can perform. 3D sculpting is mainly used to create highly detailed video game characters.
-
Scan-based Modeling
Another interesting way of modeling in 3D is the scan-based technique, where 3D scanners are utilized to scan a physical object and generate 3D replicas. There are several types of 3D scanners that involve high levels of technology. Such as structured light scanners, time-of-flight scanners, triangulation-based laser scanners, etc. All these technologies are used to scan different objects, ranging from humans, animals, environments, and the like. Even smartphones and other hand-held devices with built-in sensors can be used to scan a physical object and then create a 3D representation that can be used for various purposes (CGI, quality checking, reverse engineering, prototyping, preservation, etc.).
-
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is a relatively new 3D modeling technique that has been conserved only for a few applications. As it is understood from the name, photogrammetry mainly involves photos. Multiple photographs of the physical object are taken from all angles and under proper lighting conditions. These 2D photos or images are imported into a computer program or modeling software. The software uses algorithms to interpret the shape and dimensions of the object. Finally, a 3D representation or a 3D model is generated.
Uses of 3D modeling across multiple industries and sectors
3D technology is in full swing with its diverse benefits across multiple industries and sectors. Right from entertainment, video games, and fashion to architecture, healthcare, real estate and more. The best part of 3D models is one can also use them for 3D rendering, simulation, or printing, which helps in rapid prototyping, or visualizing a concept before construction. That said, there is a plethora of 3D modeling benefits across multiple industries.
Various types of 3D file formats
There are hundreds of confirmed and certified file formats for anything delivered in 3D. These are used to store information about the 3D models generated. Some of the most commonly used 3D file formats are OBJ, FBX, GLB, DAE, etc. Each of these formats is distinct from the others for specific reasons.
From gaming and advertising to additive manufacturing to architectural designs (BIM files), these file formats are widely used to store model information (geometry, scenes, lighting, color, texture, etc.), as well as make the models usable by other software.
Conclusion
As we reach the end of our comprehensive guide to 3D and everything about it, it is quite understandable that the technology is still evolving. Because of the multiple benefits of 3D modeling, it has undoubtedly made its way into more and more mainstream industries and influenced our daily lives with better visual representations.
With 3D modeling and rendering technologies, it has become easier to visualize a construction in its early stages and identify potential errors. Or virtually stage a vacant property for prospective buyers, or amplify furniture sales by showcasing the items through 3D product viewers or configurators. These examples of 3D modeling show the massive influence it has on modern business.
Likewise, there is software that helps 3D artists and professionals do their jobs accurately. If you want to know more about the best 3D modeling software.
For new-age digital marketers, teaming up with a third-party professional agency offering stellar 3D modeling services and solutions is always recommended. These agencies have highly trained and skilled experts who can deliver the utmost quality at an affordable rate. Start your journey with 3D technology today, and keep visiting our blog for useful information. Good luck!